
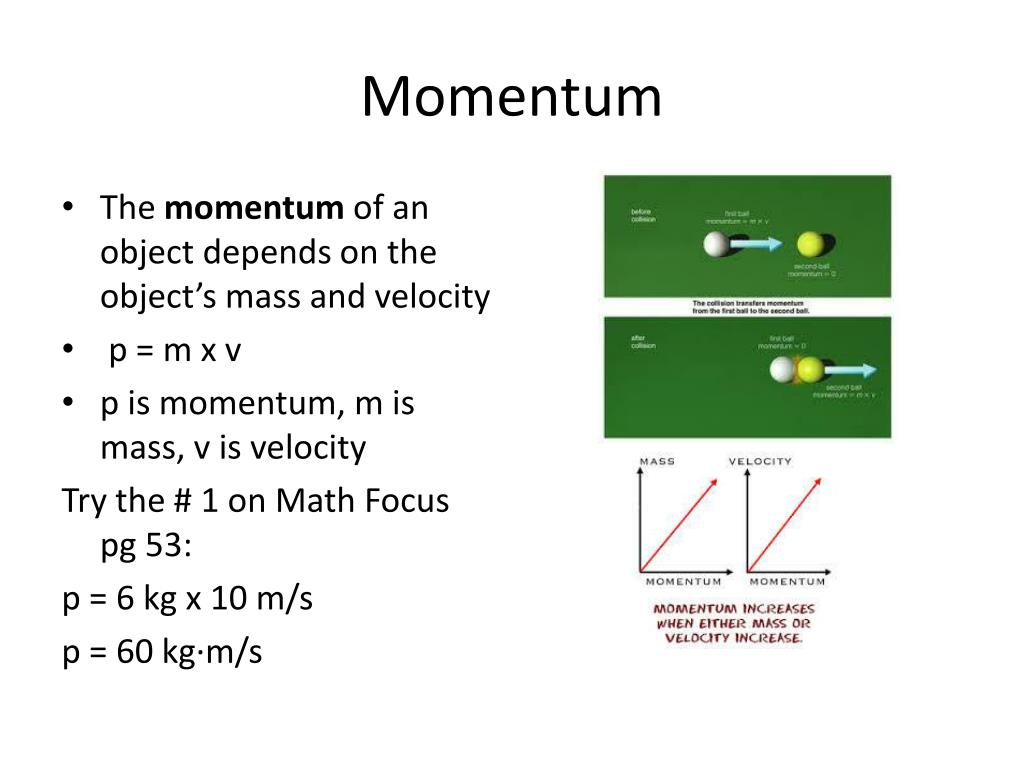
Moreover, based on finite element theory, the finite element models of the carriage and the door frame in the new tapping vehicle were built. Based on solving the interface technology between ADAMS and AMEsim software, the cosimulation model of the mechanicalelectronichydraulic combined system for the new tapping vehicle was set up, and the cosimulation of climbing 10% slope was completed. Its hydraulic and controlling models were established by utilizing AMEsim software.
#POINT IMPULSIVE FORCE SOFTWARE#
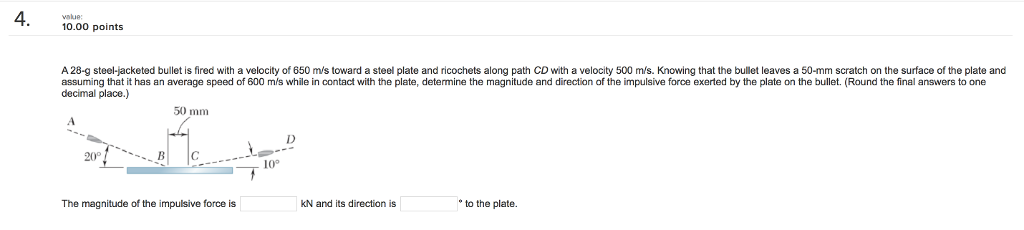
The method proposed, based on the viscoelastic model given by Hunt and Crossley, can be extended to the elasto–visco–plastic nonlinear impact model.īy using ADAMS software based on multirigidbody dynamics theory, the multirigidbody dynamics model of new tapping vehicle transporting, loading and unloading electrolytic aluminium was built. This algorithm avoids the large calculus volume required by solving the transcendental equations and definite integrals present in the mathematical model. The simplified algorithm for the calculus of viscoelastic impact parameters is also presented. For smaller values of the coefficient of restitution, the results of the present paper are in good agreement only to the Flores model. For quasi-elastic collisions, the results are practically the same for the three models. time and hysteresis loop) are compared to two models due to Lankarani and Flores. The results (variations of approach, velocity, force vs.
The effect of coefficient of restitution upon all collision characteristics is emphasized, presenting importance for the compliant materials, in the domain of small coefficients of restitution.
Then, all impact parameters can be calculated. In the present paper, the differential equation is written under a convenient form it is shown that it can be integrated and a first integral is found-this being the main asset of the work. In order to solve the problem, in the literature, there are accepted different supplementary hypotheses based on energy considerations. There is only a single available equation obtained from the theorem of momentum. The motion of the system is described by a nonlinear Hunt–Crossley equation that, when compared to the linear model, presents the advantage of a hysteresis loop closing in origin. The contact period has two phases, compression and restitution, delimited by the moment corresponding to maximum deformation. The paper presents an analytical solution for the centric viscoelastic impact of two smooth balls. In either case, at the point of external impact, the terminal impulse is obtained from the energetic coefficient of restitution.
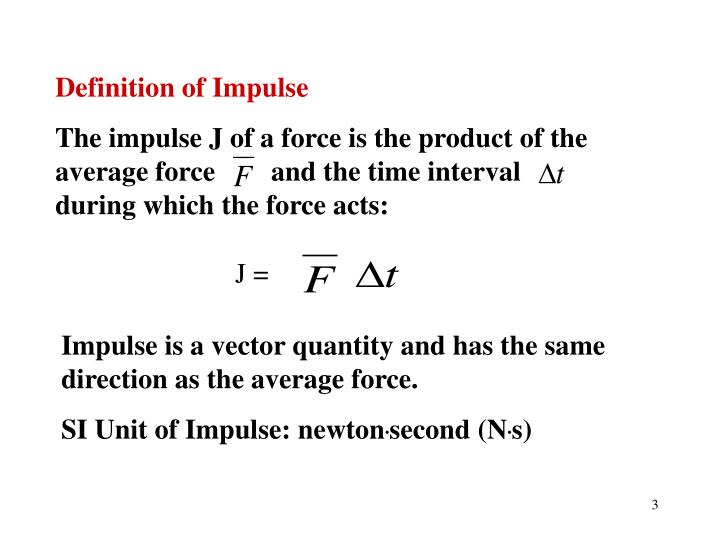
If the direction of slip is constant, however, it is more convenient to use the integrated form of this generalized impulse-momentum relation. When applied to impact between systems of hard bodies for which there is friction and slip that changes direction during contact, the differential relation is required. If the forces act impulsively (i.e., there is a negligibly small period of force application), the differentials of generalized momentum and generalized impulse are equal, and if the forces are proportional during the “period” of application, then integration of this equation gives a change of state.
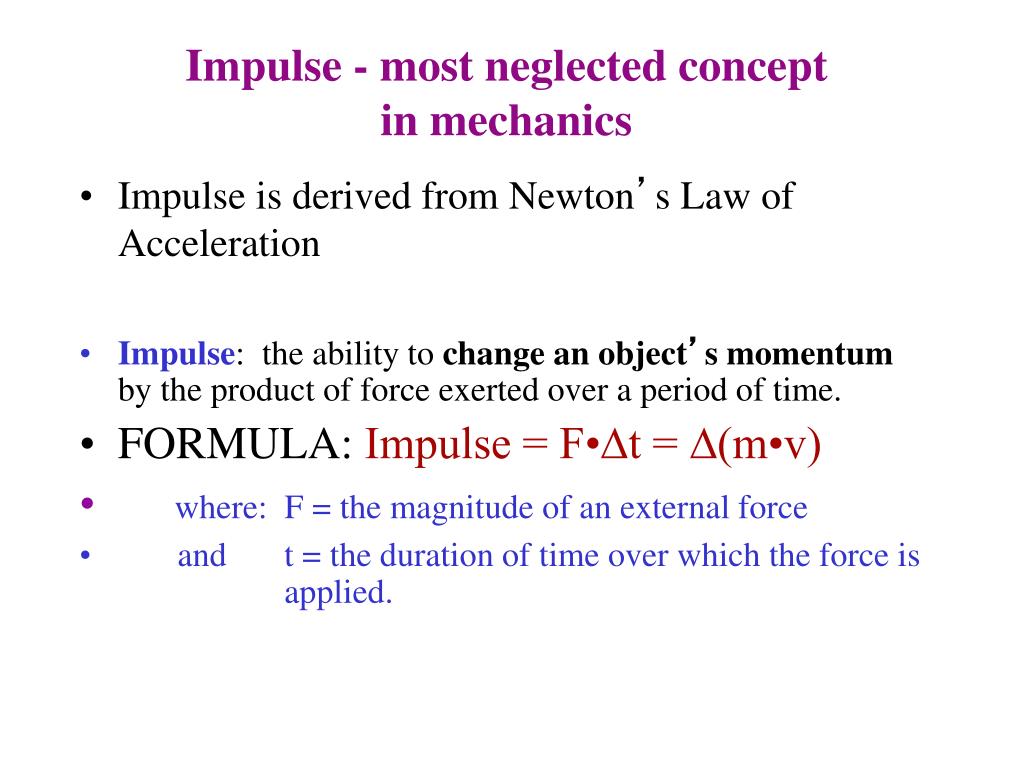
The generalized impulse vector Πι associated with these impulses has a differential d, where are velocities of the points at which the impulses are applied. If the system is subject to a set of time-dependent external forces Fj that act at locations rj, these forces result in differential impulses dpj = Fjdt. The generalized momentum of the system is defined as a vector. A mechanism composed of rigid bodies joined by ideal nondissipative pinned joints has a configuration that can be described in terms of generalized coordinates qi and time t the system has a kinetic energy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
